|
||||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
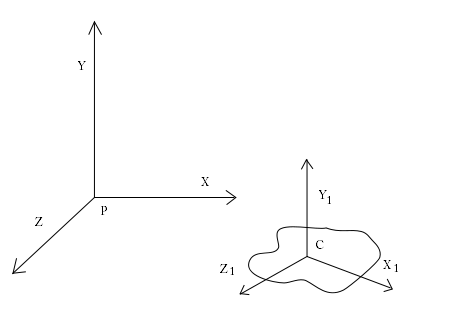
TRANSFER THEOREM FOR PRODUCTS OF INERTIA
To transform the products of inertia to a different reference frame, the transfer theorem for products of inertia is used.
In this instance, the products of inertia in the reference frame originating at point c, with the axes denoted by a *, is known. When transforming the products of inertia in relation to point C to be in relation to point P, as seen in figure 1↑, the product of inertia, IPxy can be calculated by:
(1)
Ipxy
=
− ⌠⌡(xy)dm
=
− ⌠⌡(x* + xcp)(y* + ycp)dm
=
− ⌠⌡(x* + y*)dm − xcpycp⌠⌡dm − xcp⌠⌡y*dm − ycp⌠⌡x*dm
where xcp and ycp are the respective distances between p and c in respect to the inertial frame of reference. By the virtue of the definition of center of mass, − xcp∫y*dm − ycp∫x*dm disappears. Thus,
Ipxy
=
− ⌠⌡(x*y*)dm − mxcpycp
=
ICxy − mxcpycp
Similarly, this can be applied to the other products of inertia:
Ipxz
=
ICxz − mxcpzcp
Ipyz
=
ICyz − mycpzcp
This theorem is useful in converting the products of inertia measured in the inertial frame to a body fixed frame, which simplifies calculations when the body is in motion.